Revolutionizing Earth Observation: How AI is Transforming Geospatial Intelligence
By The Satellogic Team
Exploring the Transformative Impact of AI on Geospatial Intelligence: Enhancing Earth Observation for Timely Decision-Making in Critical Situations.
In a rapidly evolving world where technology continuously pushes boundaries, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with Earth Observation (EO) platforms marks a revolutionary step forward. The recent webinar titled “Leveraging AI for Earth Observation Applications” hosted by Jack Kuhl, research director at Payload, brought together experts from NVIDIA, Satellogic, and AGO Spatial to discuss the transformative potential of AI in geospatial applications. Representing Satellogic, CEO Emiliano Kargieman and Chief Innovation Officer Gerardo Richarte provided an in-depth look into how Satellogic is leading the charge in this arena.
Addressing Key Challenges in Earth Observation
Emiliano Kargieman opened the discussion by identifying three primary barriers to the mass adoption of EO data:
- Cost: Historically, high-resolution imagery has been prohibitively expensive, while low-resolution imagery, though free, offers limited detail.
- Availability: Competing interests for satellite time often restrict data access, making it challenging to obtain timely information.
- Usability: Transforming raw satellite data into actionable insights remains complex, requiring advanced processing capabilities.
Satellogic’s Innovative Solutions
To overcome these challenges, Satellogic is building a large constellation of satellites aimed at remapping the Earth in high resolution. By creating a comprehensive catalog of updated data, they aim to make EO data accessible and affordable. Emiliano emphasized that Satellogic’s approach is designed to address the dual bottlenecks of cost and availability, enabling more widespread use of high-resolution satellite imagery.
Leveraging AI for Enhanced Usability
One of the most exciting developments at Satellogic is the application of multimodal foundation models to simplify data interaction and extraction. These models, trained on high-resolution satellite imagery, can process and analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. Emiliano explained that this capability significantly lowers the barriers to building applications on top of satellite imagery, facilitating faster and more efficient development of solutions.
Demonstration of AI Capabilities
Gaia, soon to be integrated into our platform, is a conversational application that allows users to interact with and explore the satellite data catalog through natural language queries. This tool enables users to visualize, analyze, and download specific data sets, highlighting the platform’s potential to streamline access to updated and relevant EO data. The UX design was developed so that people can use Gaia to explore the catalog and find what they want. Once they reach the data and view what they need, they can either further explore it in our Aleph platform, turn the findings into APIs or embed visualizations in other pages. The download feature allows users to either download the data for integration into their analysis or get an API call that provides refreshed data every time they request it. For instance, if a user queries “how many airplanes in the last 6 months in Los Angeles,” they will receive an updated number every time. Additionally, the “open in new window” button enables users to get the right URL to embed tables or maps into dashboards, blog posts, or live reports, with data that updates in real-time. Essentially, Gaia also serves as a way to create custom data API endpoints and data display widgets from our catalog. Below, we have included a series of videos to highlight key features of Gaia.
Two Key Aspects of AI at Satellogic
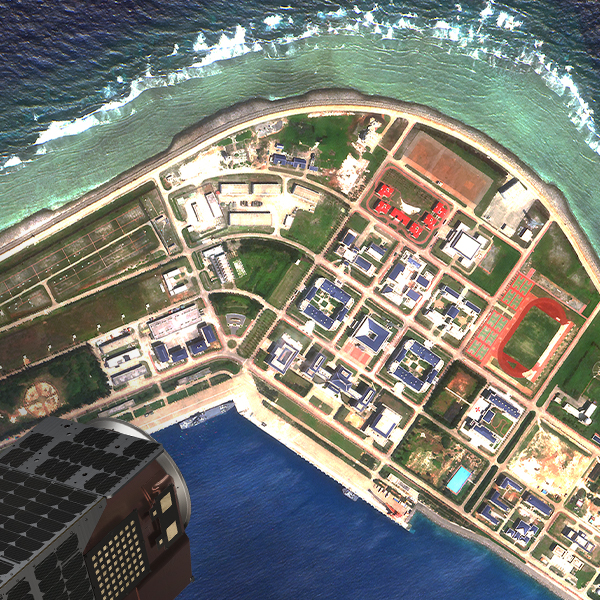
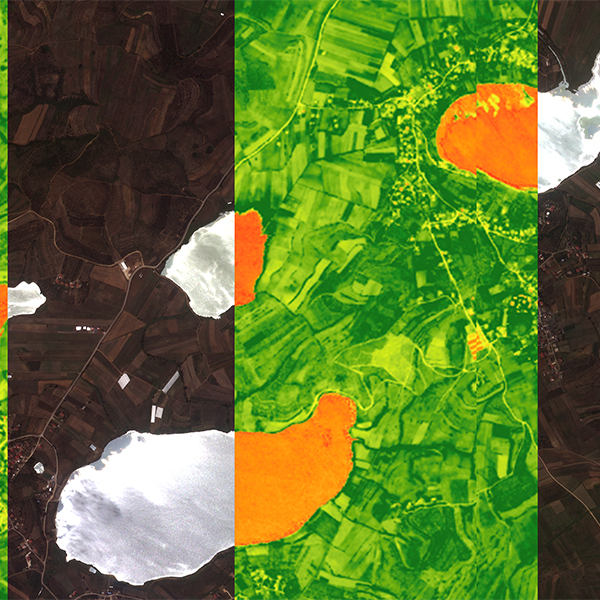
1. User Assistance in Catalog Exploration: Our Aleph platform offers multiple ways to access and explore our extensive catalog, and task future captures. Users can utilize Aleph’s web interface for direct interaction, or Aleph’s API to automate searches and integrate with their applications. Additionally, our conversational AI interface significantly enhances user experience by facilitating more intuitive and efficient access to the data, making it easier to find and utilize the information they need. Gaia also uses AI to interpret image content, for example for object detection, as showcased in the video below.
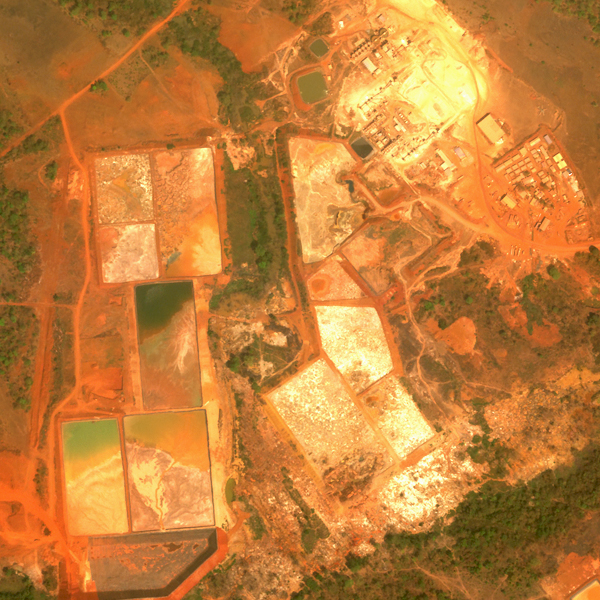
2. Insight Extraction: Our AI technology excels in extracting valuable insights by detecting objects such as roads, boats, and planes. Unlike static sources like OpenStreetMap, which are not regularly updated, our system ensures continuous updates with every new image captured. This allows for real-time monitoring and alerts, such as an increase in the number of boats in a specific area, providing dynamic and timely information. Gaia can run an analysis on an image to showcase its contents and assess changes over time, providing insights into evolving patterns and trends, both in images and analysis results, as highlighted by the video below.
Real-Time Data Processing and Alerts
One of the key advantages of Satellogic’s approach is the ability to process data in near real-time as soon as data is downloaded. Additionally by integrating AI with onboard processing capabilities, Satellogic can perform preliminary analyses directly in orbit. This reduces the need for extensive downlink bandwidth and speeds up the delivery of critical insights.
Gerardo noted that this capability is particularly valuable for applications requiring timely data, such as monitoring natural disasters or providing situational awareness in rapidly evolving ground operations.
Opening Up Access to Data
Satellogic is committed to democratizing access to EO data. Emiliano announced that they will soon open up their catalog to the public, allowing anyone to access high-resolution satellite imagery through APIs and a user-friendly web interface. This move is designed to foster innovation and enable a broader range of users to leverage EO data for various applications. Gaia can perform insight extraction on images through object detection, allowing users to identify key elements and download the data for integration into their applications. Take a look at how to integrate Gaia into your own applications.
The Future of Earth Observation with Satellogic
Looking ahead, Satellogic envisions a future where Earth Observation data is easily accessible and widely used across multiple industries. The integration of AI and advanced processing capabilities will continue to play a crucial role in this vision. Emiliano highlighted the importance of building a robust ecosystem that includes foundation models, compute power, data availability, and application development.
In conclusion, the webinar underscored Satellogic’s pioneering role in enhancing geospatial applications through AI. By addressing the key challenges of cost, availability, and usability, and by leveraging cutting-edge technologies, Satellogic is making significant strides towards making high-resolution EO data more accessible and actionable. As the technology landscape continues to evolve, Satellogic remains at the forefront of driving innovation in the Earth Observation industry.